No Preview Available !
www.DataSheet4U.com
NTMD3N08LR2
Advance Information
Power MOSFET
2.3 Amps, 80 Volts
N–Channel Enhancement–Mode
SO–8 Dual Package
Features
• Ultra Low On–Resistance Provides Higher Efficiency
♦ RDS(on) = 0.215 W, VGS = 10 V
♦ RDS(on) = 0.245 W, VGS = 5.0 V
• Low Reverse Recovery Losses
• Internal RG = 50 W
• Designed for Power Management Solutions in 42 V Automotive
System Applications
• IDSS and RDS(on) Specified at Elevated Temperature
• Avalanche Energy Specified
• Miniature SO–8 Surface Mount Package – Saves Board Space
• Mounting Information for SO–8 Package Provided
Applications
• Integrated Starter Alternator
• Electronic Power Steering
• Electronic Fuel Injection
• Catalytic Converter Heaters
MAXIMUM RATINGS (TJ = 25°C unless otherwise noted)
Rating
Symbol Value
Unit
Drain–to–Source Voltage
Drain–to–Source Voltage (RGS = 1.0 mW)
Gate–to–Source Voltage – Continuous
Gate–to–Source Voltage –
Non–Repetitive (tp ≤ 10 ms)
Continuous Drain Current @ TA = 25°C
Pulsed Drain Current (Note 1)
Total Power Dissipation @ TA = 25°C (Note 2)
Operating and Storage Temperature Range
VDSS
VDGR
VGS
VGSM
ID
IDM
PD
TJ, Tstg
80
80
±15
±20
2.3
25
3.1
–55 to
+175
V
V
A
W
°C
Single Pulse Drain–to–Source Avalanche
Energy – Starting TJ = 25°C (VDD = 50 Vdc,
VGS = 5.0 Vdc, Peak IL = 7.0 Apk,
L = 1.0 mH, RG = 25 W)
Thermal Resistance –
Junction–to–Ambient (Note 2)
EAS
RqJA
25 mJ
48 °C/W
Maximum Lead Temperature for Soldering TL 260 °C
Purposes for 10 Seconds
1. Pulse Test: Pulse Width = 10 ms, Duty Cycle = 2%
2. Mounted onto a 2″ square FR–4 board (1″ sq. oz. Cu 0.06″ thick single sided),
t ≤ 5 seconds
This document contains information on a new product. Specifications and information
herein are subject to change without notice.
http://onsemi.com
2.3 AMPERES
80 VOLTS
215 mΩ @ VGS = 5 V (Typ)
DUAL SO–8
CASE 751
STYLE 11
MARKING DIAGRAM
& PIN ASSIGNMENT
Source 1 1
8
Drain 1
Gate 1 2
3N08
7
Drain 1
3
Source 2
AYWW
6
Drain 2
4
Gate 2
5
Drain 2
(Top View)
3N08
A
Y
WW
= Specific Device Code
= Assembly Location
= Year
= Work Week
ORDERING INFORMATION
Device
Package
Shipping
NTMD3N08LR2
SO–8 2500/Tape & Reel
© Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC, 2002
August, 2002 – Rev. 2
1
Publication Order Number:
NTMD3N08LR2/D
NTMD3N08LR2
10
8
VDS
6
Q1
4
QT
Q2
80
70
VGS
60
50
40
30
2
0 Q3
01
2
ID = 2.3 A
TJ = 25°C
20
10
0
3 45
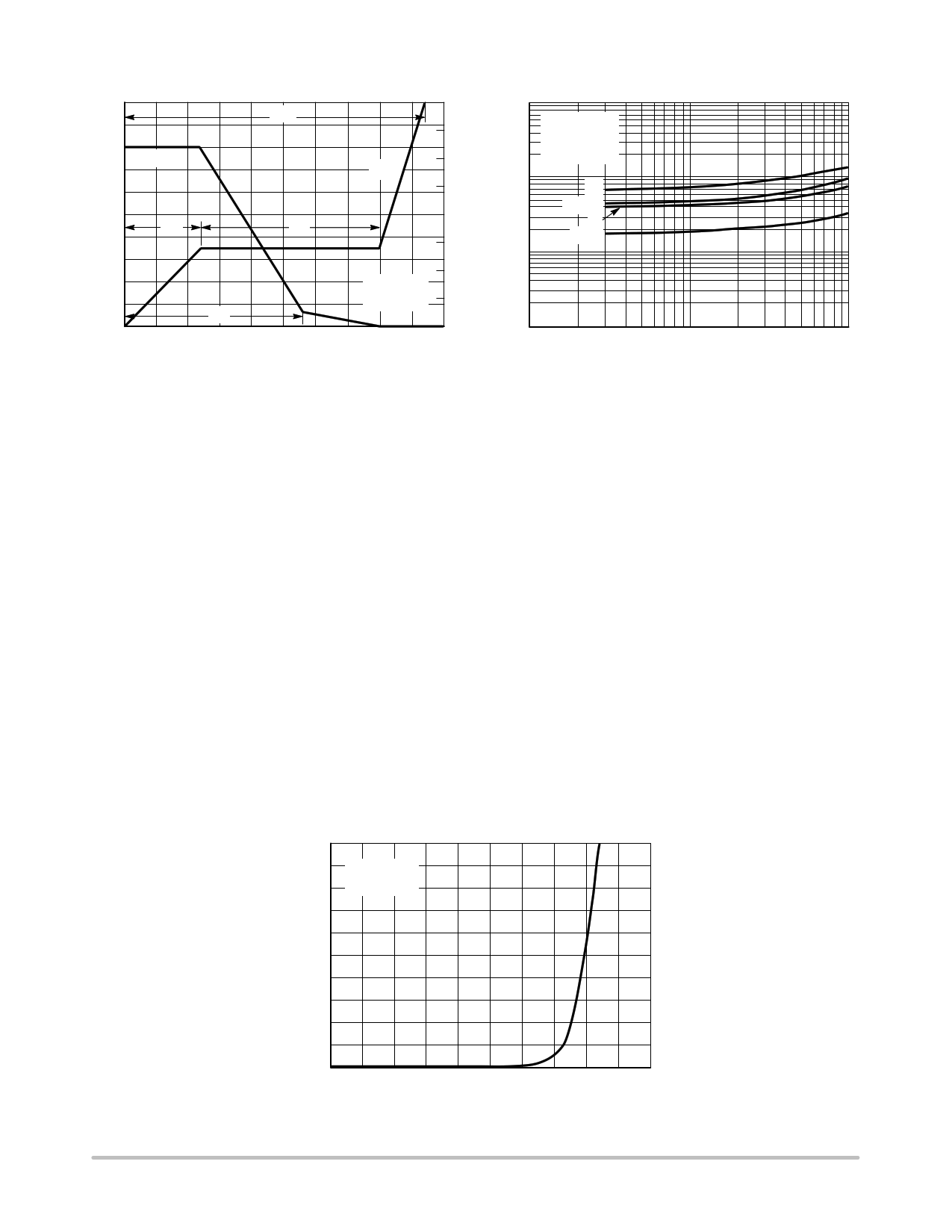
QG, TOTAL GATE CHARGE (nC)
Figure 8. Gate–To–Source and Drain–To–Source
Voltage versus Total Charge
1000
100
10
VDD = 64 V
ID = 2.3 A
VGS = 5.0 V
tr
td(off)
tf
td(on)
1
1 10 100
RG, GATE RESISTANCE (Ω)
Figure 9. Resistive Switching Time
Variation versus Gate Resistance
DRAIN–TO–SOURCE DIODE CHARACTERISTICS
The switching characteristics of a MOSFET body diode
are very important in systems using it as a freewheeling or
commutating diode. Of particular interest are the reverse
recovery characteristics which play a major role in
determining switching losses, radiated noise, EMI and RFI.
System switching losses are largely due to the nature of
the body diode itself. The body diode is a minority carrier
device, therefore it has a finite reverse recovery time, trr, due
to the storage of minority carrier charge, QRR, as shown in
the typical reverse recovery wave form of Figure 14. It is this
stored charge that, when cleared from the diode, passes
through a potential and defines an energy loss. Obviously,
repeatedly forcing the diode through reverse recovery
further increases switching losses. Therefore, one would
like a diode with short trr and low QRR specifications to
minimize these losses.
The abruptness of diode reverse recovery effects the
amount of radiated noise, voltage spikes, and current
ringing. The mechanisms at work are finite irremovable
circuit parasitic inductances and capacitances acted upon by
2.5
VGS = 0 V
2 TJ = 25°C
high di/dts. The diode’s negative di/dt during ta is directly
controlled by the device clearing the stored charge.
However, the positive di/dt during tb is an uncontrollable
diode characteristic and is usually the culprit that induces
current ringing. Therefore, when comparing diodes, the
ratio of tb/ta serves as a good indicator of recovery
abruptness and thus gives a comparative estimate of
probable noise generated. A ratio of 1 is considered ideal and
values less than 0.5 are considered snappy.
Compared to ON Semiconductor standard cell density
low voltage MOSFETs, high cell density MOSFET diodes
are faster (shorter trr), have less stored charge and a softer
reverse recovery characteristic. The softness advantage of
the high cell density diode means they can be forced through
reverse recovery at a higher di/dt than a standard cell
MOSFET diode without increasing the current ringing or the
noise generated. In addition, power dissipation incurred
from switching the diode will be less due to the shorter
recovery time and lower switching losses.
1.5
1
0.5
0
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8
VSD, SOURCE–TO–DRAIN VOLTAGE (VOLTS)
1
Figure 10. Diode Forward Voltage versus Current
http://onsemi.com
5



