
|
|
PDF AND8090 Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | AND8090 | |
| Descripción | AC Characteristics of ECL Devices | |
| Fabricantes | ON Semiconductor | |
| Logotipo | ||
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de AND8090 (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 20 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
AND8090/D
AC Characteristics of ECL
Devices
APPLICATION NOTE USAGE
This application note provides a general overview of the
AC characteristics that are specified on the
ON Semiconductor data sheets for MECL 10K™, 10H™,
100H, ECLinPS™, ECLinPS Lite™, and GigaComm™ SiGe
devices. Data sheet information takes precedence over this
application note if there are differences. This application
note includes the following information:
• AC Test Bench Information
• AC Characteristic Definitions
• AC Characteristic Test Methods
• AC Characteristic Examples
• AC Characteristic Symbols
• AC Characteristic References
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Lab Testing
Test Bench Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Test Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Test Bench Equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
AC Test Boards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Signal Levels
AC HIGH and LOW Levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Oscilloscope Averaging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Input Levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Output Levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Output Swing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Signal Timing
Duty Cycle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Maximum Input Frequency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Differential Characteristics
Differential Input Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Unused Output Termination . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Differential Crosspoint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Input Voltage Swing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Test Input Swing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
http://onsemi.com
APPLICATION NOTE
Differential Characteristics (continued)
Common Mode Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Differential Input Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Single−Ended Characteristics
Single−Ended Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Single−Ended 50% Points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Single–Ended Input Voltage Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Single–Ended Input Test Level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Differential Inputs (Single–Ended Mode) . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Timing Characteristics
Output Rise and Fall Times . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Propagation Delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Skew (Duty Cycle) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Skew (Within Device) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Skew (Device to Device) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Minimum Input Pulse Width . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Setup and Hold Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Set and Reset Recovery Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Jitter
Jitter Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Random Jitter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
RJ Confidence Levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Total RJ Test Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Test Equipment RJ Test Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
DUT RJ Calculation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Deterministic Jitter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Total DJ Test Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Test Equipment DJ Test Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
DUT DJ Calculation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Symbols and Acronyms
Symbols and Acronyms Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
References
AC Characteristic References . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
© Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC, 2003
November, 2003 − Rev. 1
1
Publication Order Number:
AND8090/D
1 page 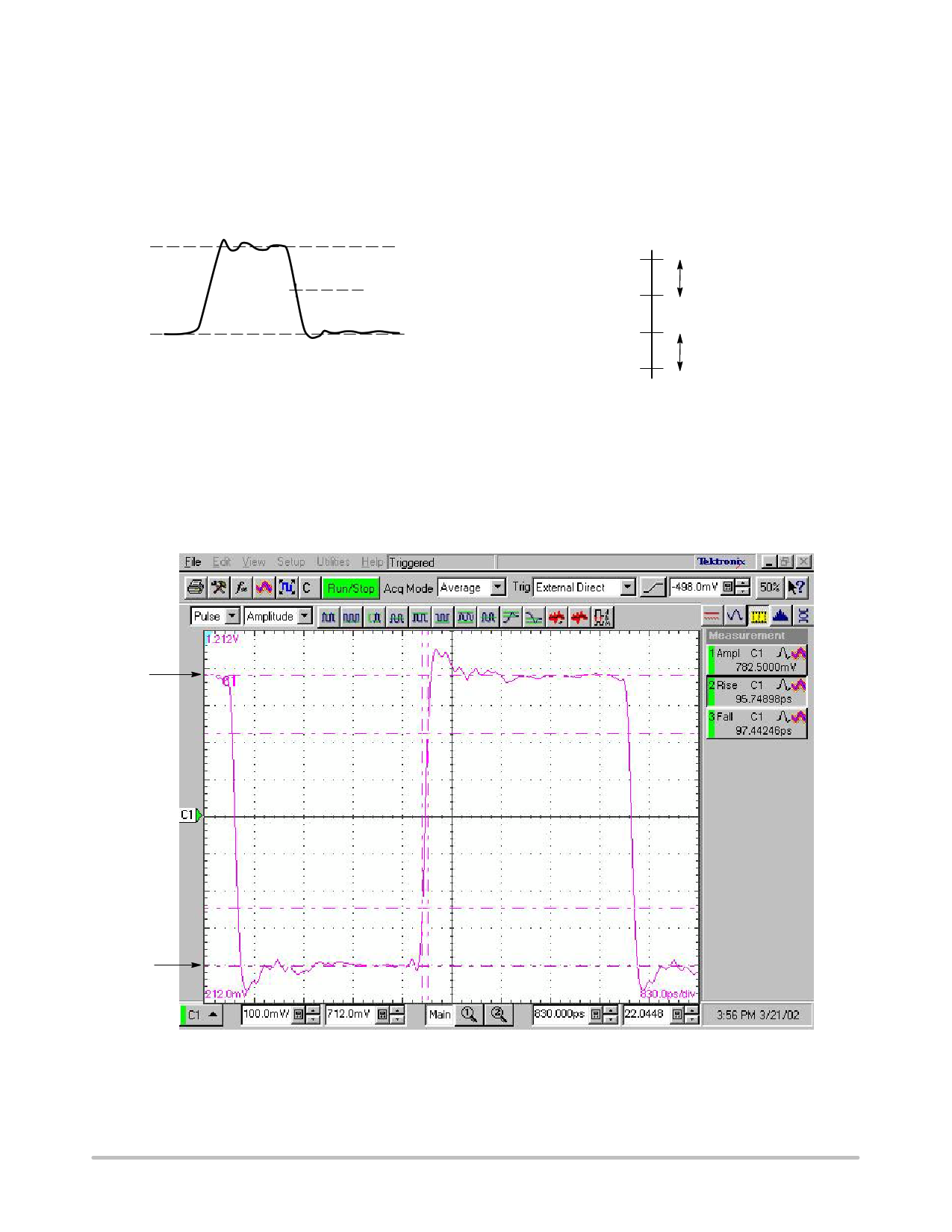
AND8090/D
SIGNAL LEVELS
AC HIGH and LOW Levels − The HIGH level referred
to in this application note corresponds to the IEEE “topline,”
and the LOW level corresponds to the IEEE “baseline” as
shown in Figure 5. The 50% point lies halfway between the
HIGH and LOW levels. Refer to IEEE Standard 194−1977
for further voltage level information.
VIH/VOH
HIGH
(topline)
50%
VIL/VOL
LOW
(baseline)
Figure 5. HIGH and LOW Waveform Definition
Input Levels − Operational differential input levels are
specified by VPP and the VIHCMR range as described in the
“Differential Characteristics” section. Operational
single−ended input levels are specified by VIL and VIH as
described in the “Single−Ended Characteristics” section.
Output Levels − Output signals may be differential or
single−ended. AC characteristics for ON Semiconductor
devices with ECL outputs are typically measured for an
output termination of 50 W to VTT (the termination voltage
equal to VCC − 2.0 V). HIGH and LOW output levels range
between the boundary and threshold values for the
respective HIGH and LOW input levels specified on data
sheets. Output logic levels are shown in Figure 6.
VOHmax
HIGH
VOHmin
Boundary
Threshold
VOLmax
LOW
VOLmin
Threshold
Boundary
Figure 6. Output Logic Levels
Oscilloscope Averaging − Digital sampling oscilloscopes
use an algorithm to determine the average level over a pulse
width to establish the HIGH and LOW levels. An example is
shown in Figure 7. The horizontal cursors at the HIGH and
LOW levels indicate the determined average levels.
HIGH
LOW
Figure 7. HIGH and LOW Waveform Levels
http://onsemi.com
5
5 Page 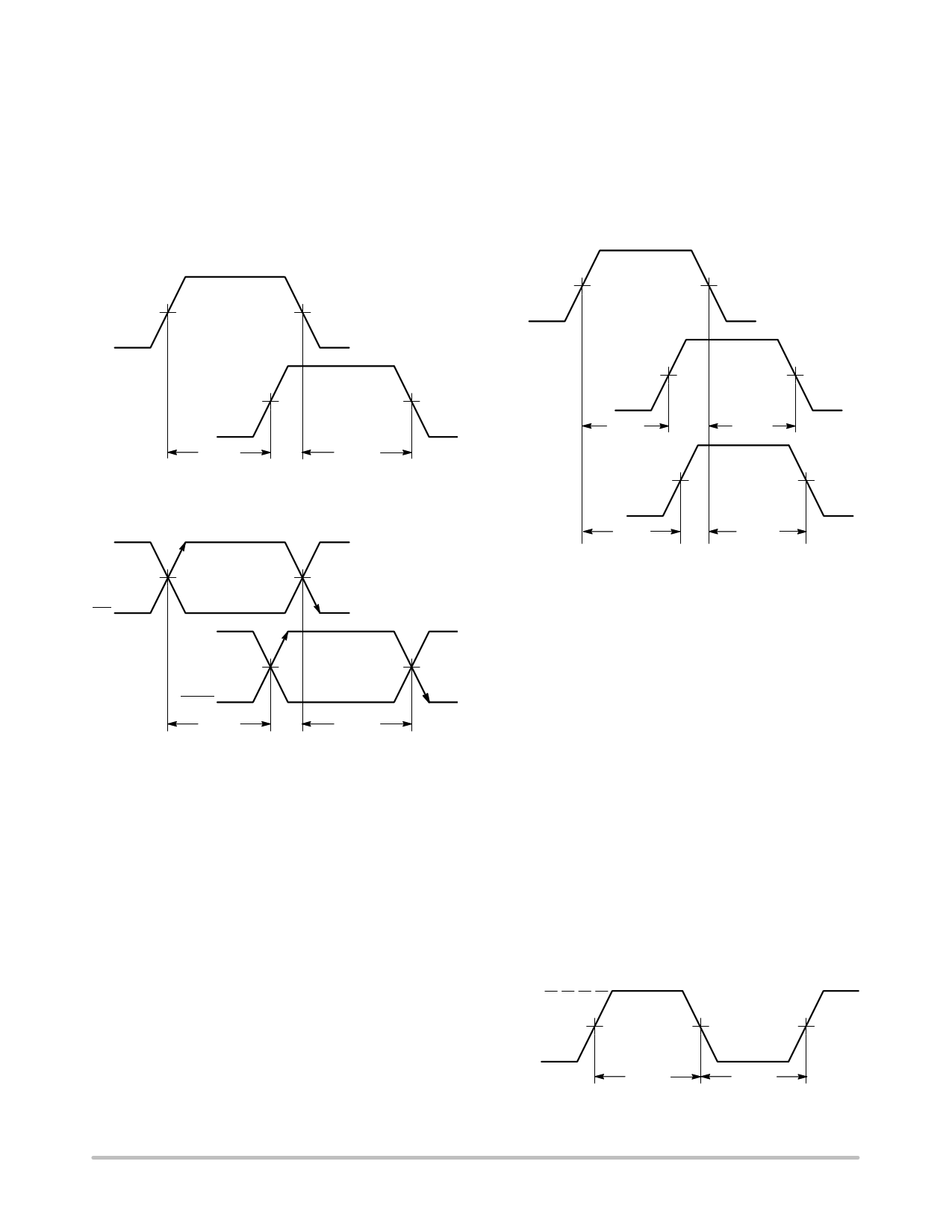
AND8090/D
Skew (Duty Cycle)
Duty cycle skew is also referred to as pulse skew. Duty
cycle skew is mathematically calculated by taking the
difference between the rising and falling edge propagation
delays. Unequal tPLH and tPHL values cause pulse width
distortion which affects the duty cycle. Duty cycle skew is
defined by the following equation and Figures 27 and 28 for
an input and its associated output.
tSKEW(Duty Cycle) + | tPLH−tPHL |
The example shown in Figure 29 defines the within
device skew parameters for a device with two inputs (D1,
D2) and their two associated outputs (Q1, Q2). The within
device skew for this example would be the higher of the
following two equation results:
tSKEW(Within Device) + tPLH2 * tPLH1
tSKEW(Within Device) + tPHL2 * tPHL1
50%
D2
50%
50%
50%
Q2
tPLH
tPHL
Figure 27. Single−Ended Duty Cycle Skew
IN2
Xpt Xpt
IN2
OUT2
Xpt
OUT2
tPLH
Xpt
tPHL
Figure 28. Differential Duty Cycle Skew
Skew (Within Device)
Within device skew is the difference between the identical
transition propagation delays of a single multiple output
device with a common input. It is mathematically calculated
by obtaining the rising and falling output propagation delays
for each individual output of the device. The minimum
output propagation delay from the set of delays is then
subtracted from the maximum output propagation delay
from the set of delays as shown in the following equations.
The higher of the two equation results is taken as the within
device skew specification.
tSKEW (Within Device Rising Edge)
+ tPLH(max from set) * tPLH(min from set)
tSKEW (Within Device Falling Edge)
+ tPHL(max from set) * tPHL(min from set)
50%
D1 = D2
50%
50%
Q1
tPLH1
tPHL1
50%
50%
50%
Q2
tPLH2
tPHL2
Figure 29. Within Device Skew
Skew (Device to Device)
Device to device skew is the difference between the
identical transition propagation delays of two devices with
a common input signal under identical operating conditions
(identical ambient temperature, VCC, VEE, etc). It is
mathematically calculated from data sheet propagation
delay values as shown below.
tSKEW (Device to Device) + tPLH(max) * tPLH(min)
+ tPHL(max) * tPHL(min)
Minimum Input Pulse Width
The minimum input pulse width (tPW) is the shortest pulse
width that will guarantee proper device operation. It is
measured by decreasing the test signal generator pulse width
(i.e., DUT input pulse width) until the DUT outputs no
longer function properly. For single−ended inputs, it is
measured between the 50% points of the rise and fall
transitions as shown in Figure 30.
VIH
50%
VIL
tPW
tPW
Figure 30. Single−Ended Input Pulse Width
http://onsemi.com
11
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 20 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet AND8090.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| AND8090 | AC Characteristics of ECL Devices | ON Semiconductor |
| AND8090D | AC Characteristics of ECL Devices | ON Semiconductor |
| AND8094 | Three New Tiny Switches Facilitate Video Switching | ON Semiconductor |
| AND8094D | Three New Tiny Switches Facilitate Video Switching | ON Semiconductor |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |
